Web3.js JavaScript Library¶
Introduction¶
Web3.js is a set of libraries that allow developers to interact with Ethereum nodes using HTTP, IPC, or WebSocket protocols with JavaScript. Tanssi-powered EVM networks have an Ethereum-like API that is fully compatible with Ethereum-style JSON RPC invocations. Therefore, developers can leverage this compatibility and use the Web3.js library to interact with a Tanssi EVM network node as if they were doing so on Ethereum. For more information on Web3.js, check out their documentation site.
In this guide, you'll learn how to set up the Web3.js library for your Tanssi EVM network. Next, to showcase the library in action, you'll use the Web3.js library to send a transaction and deploy a contract on a Tanssi demo EVM network running on Dancelight. This guide can be adapted for your own Tanssi EVM network by simply changing the endpoint.
Note
The examples in this guide are based on a MacOS or Ubuntu 20.04 environment. If you're using Windows, you'll need to adapt them accordingly.
Furthermore, please ensure that you have Node.js and a package manager (such as npm or yarn) installed. To learn how to install Node.js, please check their official documentation.
Also, make sure you've initialized a package.json file for ES6 modules. You can initialize a default package.json file using npm by running the following command npm init --yes.
Checking Prerequisites¶
For the examples in this guide, you will need to have the following:
- An account with funds in the Tanssi EVM network you are testing with
Installing Web3Js¶
For this guide, you'll need to install the Web3.js library and the Solidity compiler. To install both NPM packages, you can run the following command:
npm install web3 solc@0.8.0
yarn add web3 solc@0.8.0
Setting up the Web3 Provider¶
Throughout this guide, you'll be creating a bunch of scripts that provide different functionality such as sending a transaction, deploying a contract, and interacting with a deployed contract. In most of these scripts you'll need to create an Web3.js provider to interact with the network.
To set up a Web3 provider, you can take the following steps:
- Import the
Web3library. - Create the Web3 provider and specify the RPC url. You can configure Web3.js to work with the Tanssi demo EVM network running on Dancelight, or your own Tanssi EVM network by simply changing the endpoint.
// 1. Import Web3
const Web3 = require('web3');
// 2. Create Web3 provider and insert your RPC url
const web3 = new Web3(
'https://services.tanssi-testnet.network/dancelight-2001/'
);
Save this code snippet as you'll need it for the scripts that are used in the following sections.
Send a Transaction¶
During this section, you'll be creating a couple of scripts. The first one will be to check the balances of your accounts before trying to send a transaction. The second script will actually send the transaction.
You can also use the balance script to check the account balances after the transaction has been sent.
Check Balances Script¶
You'll only need one file to check the balances of both addresses before and after the transaction is sent. To get started, you can create a balances.js file by running:
touch balances.js
Next, you will create the script for this file and complete the following steps:
- Set up the Web3 provider
- Define the
addressFromandaddressTovariables - Create the asynchronous
balancesfunction which wraps theweb3.eth.getBalancemethod - Use the
web3.eth.getBalancefunction to fetch the balances for theaddressFromandaddressToaddresses. You can also leverage theweb3.utils.fromWeifunction to transform the balance into a more readable number inTANGO - Lastly, run the
balancesfunction
// 1. Add the Web3 provider logic here:
// {...}
// 2. Create address variables
const addressFrom = 'INSERT_ADDRESS_FROM';
const addressTo = 'INSERT_ADDRESS_TO';
// 3. Create balances function
const balances = async () => {
// 4. Fetch balance info
const balanceFrom = web3.utils.fromWei(
await web3.eth.getBalance(addressFrom),
'ether'
);
const balanceTo = web3.utils.fromWei(
await web3.eth.getBalance(addressTo),
'ether'
);
console.log(`The balance of ${addressFrom} is: ${balanceFrom} TANGO`);
console.log(`The balance of ${addressTo} is: ${balanceTo} TANGO`);
};
// 5. Call balances function
balances();
View the complete script
// Import Web3
const Web3 = require('web3');
// Add the Web3 provider logic here:
const providerRPC = {
evmNetwork: 'https://services.tanssi-testnet.network/dancelight-2001', // Insert your RPC URL here
};
const web3 = new Web3(providerRPC.evmNetwork);
// Create address variables
const addressFrom = 'INSERT_ADDRESS_FROM';
const addressTo = 'INSERT_ADDRESS_TO';
// Create balances function
const balances = async () => {
// Fetch balance info
const balanceFrom = web3.utils.fromWei(
await web3.eth.getBalance(addressFrom),
'ether'
);
const balanceTo = web3.utils.fromWei(
await web3.eth.getBalance(addressTo),
'ether'
);
console.log(`The balance of ${addressFrom} is: ${balanceFrom} TANGO`);
console.log(`The balance of ${addressTo} is: ${balanceTo} TANGO`);
};
// Call balances function
balances();
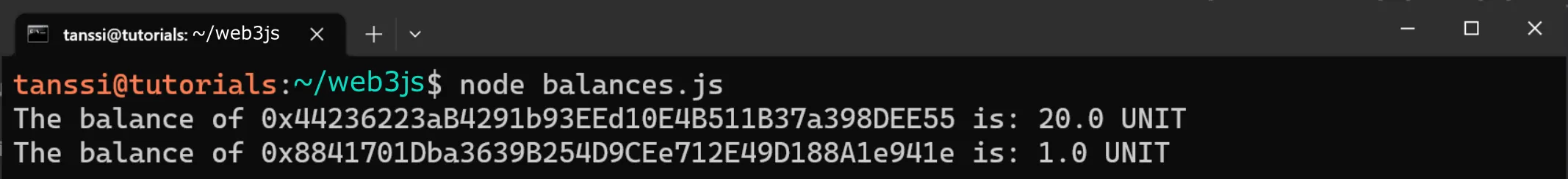
To run the script and fetch the account balances, you can run the following command:
node balances.js
If successful, the balances for the origin and receiving address will be displayed in your terminal in ETH.
Send Transaction Script¶
You'll only need one file to execute a transaction between accounts. For this example, you'll be transferring 1 TANGO token from an origin address (from which you hold the private key) to another address. To get started, you can create a transaction.js file by running:
touch transaction.js
Next, you will create the script for this file and complete the following steps:
- Set up the Web3 provider
- Define the
addressFrom, including theprivateKey, and theaddressTovariables. The private key is required to create a wallet instance. Note: This is for example purposes only. Never store your private keys in a JavaScript file - Create the asynchronous
sendfunction, which wraps the transaction object, and the sign and send transaction functions - Create and sign the transaction using the
web3.eth.accounts.signTransactionfunction. Pass in thegas,addressTo, andvaluefor the transaction along with the sender'sprivateKey - Send the signed transaction using the
web3.eth.sendSignedTransactionmethod and pass in the raw transaction. Then useawaitto wait until the transaction is processed and the transaction receipt is returned - Lastly, run the
sendfunction
// 1. Add the Web3 provider logic here:
// {...}
// 2. Create account variables
const accountFrom = {
privateKey: 'INSERT_YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY',
address: 'INSERT_PUBLIC_ADDRESS_OF_PK',
};
const addressTo = 'INSERT_ADDRESS_TO'; // Change to address
// 3. Create send function
const send = async () => {
console.log(
`Attempting to send transaction from ${accountFrom.address} to ${addressTo}`
);
// 4. Sign tx with PK
const createTransaction = await web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction(
{
gas: 21000,
to: addressTo,
value: web3.utils.toWei('1', 'ether'),
},
accountFrom.privateKey
);
// 5. Send tx and wait for receipt
const createReceipt = await web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(
createTransaction.rawTransaction
);
console.log(
`Transaction successful with hash: ${createReceipt.transactionHash}`
);
};
// 6. Call send function
send();
View the complete script
// Import Web3
const Web3 = require('web3');
// Add the Web3 provider logic here:
const providerRPC = {
evmNetwork: 'https://services.tanssi-testnet.network/dancelight-2001', // Insert your RPC URL here
};
const web3 = new Web3(providerRPC.evmNetwork);
// Create account variables
const accountFrom = {
privateKey: 'INSERT_YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY',
address: 'INSERT_PUBLIC_ADDRESS_OF_PK',
};
const addressTo = 'INSERT_ADDRESS_TO';
// Create send function
const send = async () => {
console.log(
`Attempting to send transaction from ${accountFrom.address} to ${addressTo}`
);
// Sign tx with PK
const createTransaction = await web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction(
{
gas: 21000,
to: addressTo,
value: web3.utils.toWei('1', 'ether'),
},
accountFrom.privateKey
);
// Send tx and wait for receipt
const createReceipt = await web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(
createTransaction.rawTransaction
);
console.log(
`Transaction successful with hash: ${createReceipt.transactionHash}`
);
};
// Call send function
send();
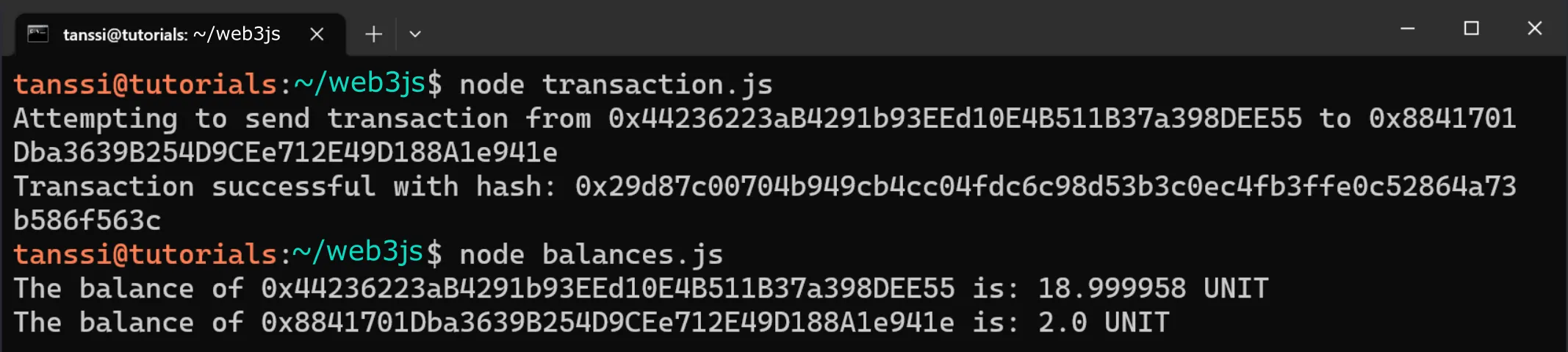
To run the script, you can run the following command in your terminal:
node transaction.js
If the transaction was successful, in your terminal, you'll see the transaction hash has been printed out.
You can also use the balances.js script to check that the balances for the origin and receiving accounts have changed. The entire workflow would look like this:
Deploy a Contract¶
The contract you'll be compiling and deploying in the next couple of sections is a simple incrementer contract, arbitrarily named Incrementer.sol. You can get started by creating a file for the contract:
touch Incrementer.sol
Next, you can add the Solidity code to the file:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Incrementer {
uint256 public number;
constructor(uint256 _initialNumber) {
number = _initialNumber;
}
function increment(uint256 _value) public {
number = number + _value;
}
function reset() public {
number = 0;
}
}
The constructor function, which runs when the contract is deployed, sets the initial value of the number variable stored on-chain (default is 0). The increment function adds the _value provided to the current number, but a transaction needs to be sent, which modifies the stored data. Lastly, the reset function resets the stored value to zero.
Note
This contract is a simple example for illustration purposes only.
Compile Contract Script¶
In this section, you'll create a script that uses the Solidity compiler to output the bytecode and interface (ABI) for the Incrementer.sol contract. To get started, you can create a compile.js file by running:
touch compile.js
Next, you will create the script for this file and complete the following steps:
- Import the
fsandsolcpackages - Using the
fs.readFileSyncfunction, you'll read and save the file contents ofIncrementer.soltosource - Build the
inputobject for the Solidity compiler by specifying thelanguage,sources, andsettingsto be used - Using the
inputobject, you can compile the contract usingsolc.compile - Extract the compiled contract file and export it to be used in the deployment script
// 1. Import packages
import fs from 'fs';
import solc from 'solc';
// 2. Get path and load contract
const source = fs.readFileSync('Incrementer.sol', 'utf8');
// 3. Create input object
const input = {
language: 'Solidity',
sources: {
'Incrementer.sol': {
content: source,
},
},
settings: {
outputSelection: {
'*': {
'*': ['*'],
},
},
},
};
// 4. Compile the contract
const tempFile = JSON.parse(solc.compile(JSON.stringify(input)));
const contractFile = tempFile.contracts['Incrementer.sol']['Incrementer'];
// 5. Export contract data
export default contractFile;
Deploy Contract Script¶
With the script for compiling the Incrementer.sol contract in place, you can then use the results to send a signed transaction that deploys it. To do so, you can create a file for the deployment script called deploy.js:
touch deploy.js
Next, you will create the script for this file and complete the following steps:
- Import the contract file from
compile.js - Set up the Web3 provider
- Define the
addressFrom, including theprivateKey, and theaddressTovariables. The private key is required to create a wallet instance. Note: This is for example purposes only. Never store your private keys in a JavaScript file - Save the
bytecodeandabifor the compiled contract - Create the asynchronous
deployfunction that will be used to deploy the contract - Create the contract instance using the
web3.eth.Contractfunction - Create the constructor and pass in the
bytecodeand the initial value for the incrementer. For this example, you can set the initial value to5 - Create and sign the transaction using the
web3.eth.accounts.signTransactionfunction. Pass in thedataand thegasfor the transaction along with the sender'sprivateKey - Send the signed transaction using the
web3.eth.sendSignedTransactionmethod and pass in the raw transaction. Then useawaitto wait until the transaction is processed and the transaction receipt is returned - Lastly, run the
deployfunction
// 1. Import the contract file
const contractFile = require('./compile');
// 2. Add the Web3 provider logic here:
// {...}
// 3. Create address variables
const accountFrom = {
privateKey: 'INSERT_PRIVATE_KEY',
address: 'INSERT_PUBLIC_ADDRESS_OF_PK',
};
// 4. Get the bytecode and API
const bytecode = contractFile.evm.bytecode.object;
const abi = contractFile.abi;
// 5. Create deploy function
const deploy = async () => {
console.log(`Attempting to deploy from account ${accountFrom.address}`);
// 6. Create contract instance
const incrementer = new web3.eth.Contract(abi);
// 7. Create constructor tx
const incrementerTx = incrementer.deploy({
data: bytecode,
arguments: [5],
});
// 8. Sign transacation and send
const createTransaction = await web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction(
{
data: incrementerTx.encodeABI(),
gas: await incrementerTx.estimateGas(),
},
accountFrom.privateKey
);
// 9. Send tx and wait for receipt
const createReceipt = await web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(
createTransaction.rawTransaction
);
console.log(`Contract deployed at address: ${createReceipt.contractAddress}`);
};
// 10. Call deploy function
deploy();
View the complete script
// Import web3 and the contract file
const Web3 = require('web3');
const contractFile = require('./compile');
// Add the Web3 provider logic here
const providerRPC = {
evmNetwork: 'https://services.tanssi-testnet.network/dancelight-2001', // Insert your RPC URL here
};
const web3 = new Web3(providerRPC.evmNetwork);
// Create address variables
const accountFrom = {
privateKey: 'INSERT_PRIVATE_KEY',
address: 'INSERT_PUBLIC_ADDRESS_OF_PK',
};
// Get the bytecode and API
const bytecode = contractFile.evm.bytecode.object;
const abi = contractFile.abi;
// Create deploy function
const deploy = async () => {
console.log(`Attempting to deploy from account ${accountFrom.address}`);
// Create contract instance
const incrementer = new web3.eth.Contract(abi);
// Create constructor tx with initial value of 5
const incrementerTx = incrementer.deploy({
data: bytecode,
arguments: [5],
});
// Sign transacation and send
const createTransaction = await web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction(
{
data: incrementerTx.encodeABI(),
gas: await incrementerTx.estimateGas(),
},
accountFrom.privateKey
);
// Send tx and wait for receipt
const createReceipt = await web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(
createTransaction.rawTransaction
);
console.log(`Contract deployed at address: ${createReceipt.contractAddress}`);
};
// Call deploy function
deploy();
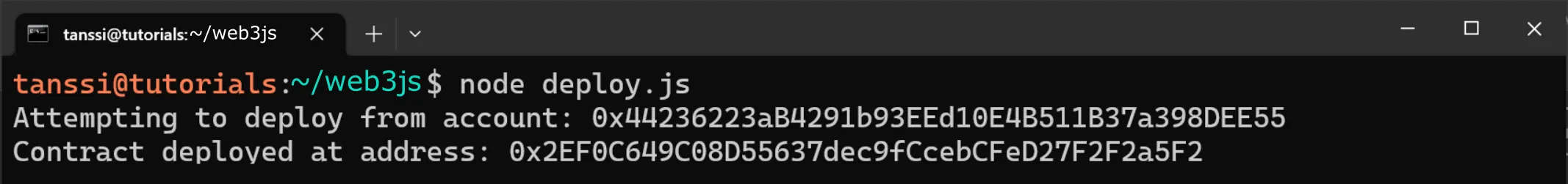
To run the script, you can enter the following command into your terminal:
node deploy.js
If successful, the contract's address will be displayed in the terminal.
Read Contract Data (Call Methods)¶
Call methods are the type of interactions that don't modify the contract's storage (change variables), meaning no transaction needs to be sent. They simply read various storage variables of the deployed contract.
To get started, you can create a file and name it get.js:
touch get.js
Then you can take the following steps to create the script:
- Import the
abifrom thecompile.jsfile - Set up the Web3 provider
- Create the
contractAddressvariable using the address of the deployed contract - Create an instance of the contract using the
web3.eth.Contractfunction and passing in theabiandcontractAddress - Create the asynchronous
getfunction - Use the contract instance to call one of the contract's methods and pass in any inputs if necessary. For this example, you will call the
numbermethod, which doesn't require any inputs. You can useawait, which will return the value requested once the request promise resolves - Lastly, call the
getfunction
// 1. Import the contract abi
const { abi } = require('./compile');
// 2. Add the Web3 provider logic here:
// {...}
// 3. Create address variables
const contractAddress = 'INSERT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS';
// 4. Create contract instance
const incrementer = new web3.eth.Contract(abi, contractAddress);
// 5. Create get function
const get = async () => {
console.log(`Making a call to contract at address: ${contractAddress}`);
// 6. Call contract
const data = await incrementer.methods.number().call();
console.log(`The current number stored is: ${data}`);
};
// 7. Call get function
get();
View the complete script
// Import web3 and the contract file
const Web3 = require('web3');
const { abi } = require('./compile');
// Add the Web3 provider logic here:
const providerRPC = {
evmNetwork: 'https://services.tanssi-testnet.network/dancelight-2001', // Insert your RPC URL here
};
const web3 = new Web3(providerRPC.evmNetwork);
// Create address variables
const contractAddress = 'INSERT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS';
// Create contract instance
const incrementer = new web3.eth.Contract(abi, contractAddress);
// Create get function
const get = async () => {
console.log(`Making a call to contract at address: ${contractAddress}`);
// Call contract
const data = await incrementer.methods.number().call();
console.log(`The current number stored is: ${data}`);
};
// Call get function
get();
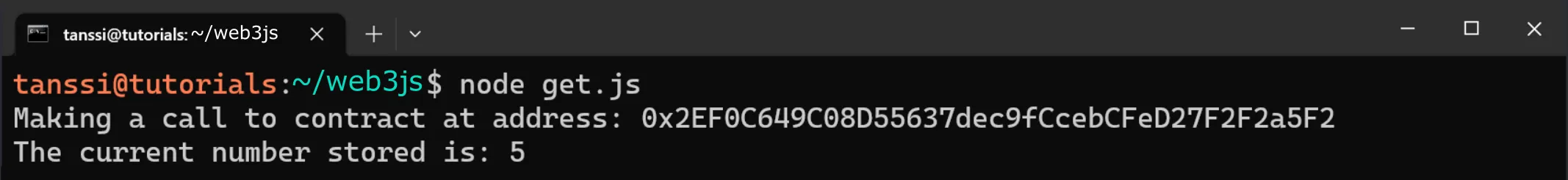
To run the script, you can enter the following command in your terminal:
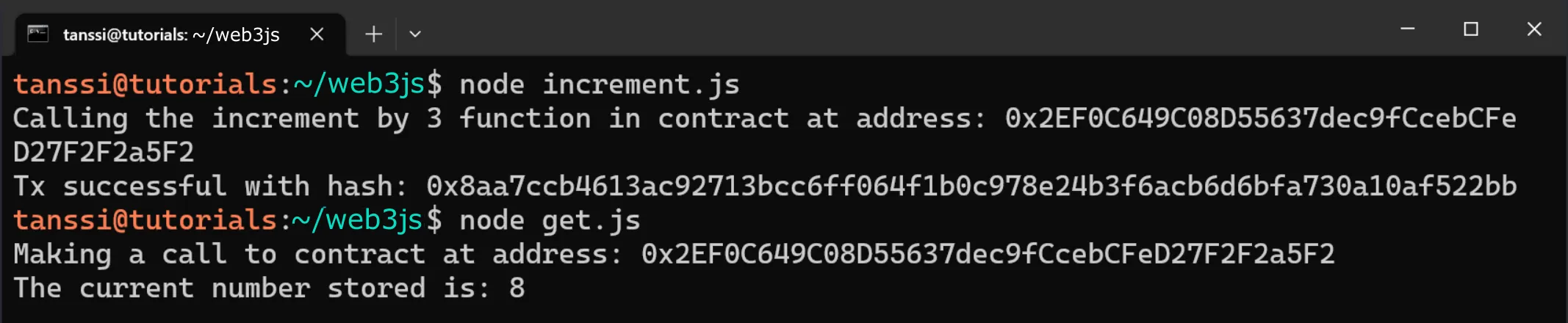
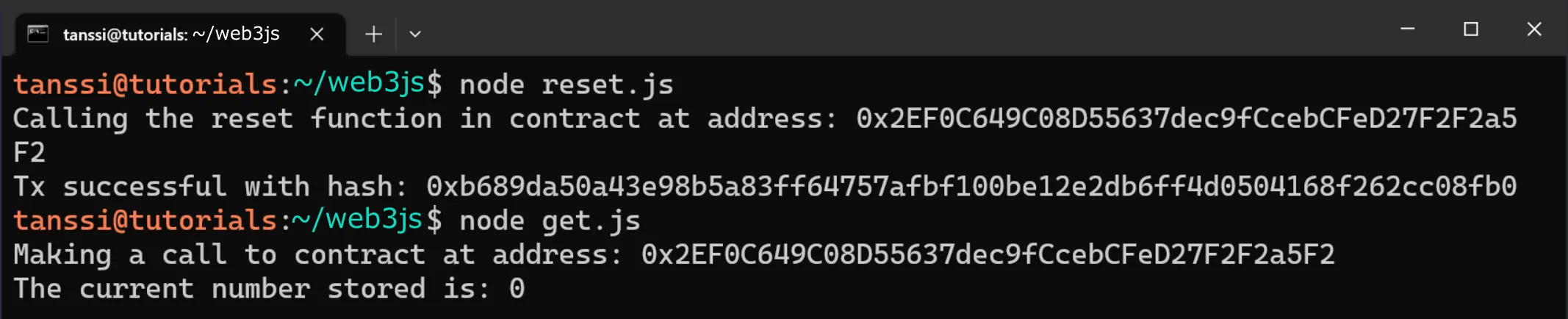
node get.js
If successful, the value will be displayed in the terminal.
Interact with Contract (Send Methods)¶
Send methods are the type of interactions that modify the contract's storage (change variables), meaning a transaction needs to be signed and sent. In this section, you'll create two scripts: one to increment and one to reset the incrementer. To get started, you can create a file for each script and name them increment.js and reset.js:
touch increment.js reset.js
Open the increment.js file and take the following steps to create the script:
- Import the
abifrom thecompile.jsfile - Set up the Web3 provider
- Define the
privateKeyfor the origin account, thecontractAddressof the deployed contract, and the_valueto increment by. The private key is required to create a wallet instance. Note: This is for example purposes only. Never store your private keys in a JavaScript file - Create an instance of the contract using the
web3.eth.Contractfunction and passing in theabiandcontractAddress - Use the contract instance to build the increment transaction using the
methods.incrementfunction and passing in the_valueas an input - Create the asynchronous
incrementfunction - Use the contract instance and the increment transaction you previously created to sign the transaction with the sender's private key. You'll use the
web3.eth.accounts.signTransactionfunction and specify thetoaddress, thedata, and thegasfor the transaction - Send the signed transaction using the
web3.eth.sendSignedTransactionmethod and pass in the raw transaction. Then useawaitto wait until the transaction is processed and the transaction receipt is returned - Lastly, call the
incrementfunction
// 1. Import the contract abi
const { abi } = require('./compile');
// 2. Add the Web3 provider logic here:
// {...}
// 3. Create variables
const accountFrom = {
privateKey: 'INSERT_YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY',
};
const contractAddress = 'INSERT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS';
const _value = 3;
// 4. Create contract instance
const incrementer = new web3.eth.Contract(abi, contractAddress);
// 5. Build increment tx
const incrementTx = incrementer.methods.increment(_value);
// 6. Create increment function
const increment = async () => {
console.log(
`Calling the increment by ${_value} function in contract at address: ${contractAddress}`
);
// 7. Sign Tx with PK
const createTransaction = await web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction(
{
to: contractAddress,
data: incrementTx.encodeABI(),
gas: await incrementTx.estimateGas(),
},
accountFrom.privateKey
);
// 8. Send Tx and Wait for Receipt
const createReceipt = await web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(
createTransaction.rawTransaction
);
console.log(`Tx successful with hash: ${createReceipt.transactionHash}`);
};
// 9. Call increment function
increment();
View the complete script
// Import Web3 and the contract abi
const Web3 = require('web3');
const { abi } = require('./compile');
// Add the Web3 provider logic here:
const providerRPC = {
evmNetwork: 'https://services.tanssi-testnet.network/dancelight-2001', // Insert your RPC URL here
};
const web3 = new Web3(providerRPC.evmNetwork);
// Create variables
const accountFrom = {
privateKey: 'INSERT_YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY',
};
const contractAddress = 'INSERT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS';
const _value = 3;
// Create contract instance
const incrementer = new web3.eth.Contract(abi, contractAddress);
// Build increment tx
const incrementTx = incrementer.methods.increment(_value);
// Create increment function
const increment = async () => {
console.log(
`Calling the increment by ${_value} function in contract at address: ${contractAddress}`
);
// Sign Tx with PK
const createTransaction = await web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction(
{
to: contractAddress,
data: incrementTx.encodeABI(),
gas: await incrementTx.estimateGas(),
},
accountFrom.privateKey
);
// Send Tx and Wait for Receipt
const createReceipt = await web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(
createTransaction.rawTransaction
);
console.log(`Tx successful with hash: ${createReceipt.transactionHash}`);
};
// Call increment function
increment();
To run the script, you can enter the following command in your terminal:
node increment.js
If successful, the transaction hash will be displayed in the terminal. You can use the get.js script alongside the increment.js script to make sure that the value is changing as expected.
Next you can open the reset.js file and take the following steps to create the script:
- Import the
abifrom thecompile.jsfile - Set up the Web3 provider
- Define the
privateKeyfor the origin account and thecontractAddressof the deployed contract. The private key is required to create a wallet instance. Note: This is for example purposes only. Never store your private keys in a JavaScript file - Create an instance of the contract using the
web3.eth.Contractfunction and passing in theabiandcontractAddress - Use the contract instance to build the reset transaction using the
methods.resetfunction - Create the asynchronous
resetfunction - Use the contract instance and the reset transaction you previously created to sign the transaction with the sender's private key. You'll use the
web3.eth.accounts.signTransactionfunction and specify thetoaddress, thedata, and thegasfor the transaction - Send the signed transaction using the
web3.eth.sendSignedTransactionmethod and pass in the raw transaction. Then useawaitto wait until the transaction is processed and the transaction receipt is returned - Lastly, call the
resetfunction
// 1. Import the contract abi
const { abi } = require('./compile');
// 2. Add the Web3 provider logic here:
// {...}
// 3. Create variables
const accountFrom = {
privateKey: 'INSERT_YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY',
};
const contractAddress = 'INSERT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS';
// 4. Create Contract Instance
const incrementer = new web3.eth.Contract(abi, contractAddress);
// 5. Build reset tx
const resetTx = incrementer.methods.reset();
// 6. Create reset function
const reset = async () => {
console.log(
`Calling the reset function in contract at address: ${contractAddress}`
);
// 7. Sign tx with PK
const createTransaction = await web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction(
{
to: contractAddress,
data: resetTx.encodeABI(),
gas: await resetTx.estimateGas(),
},
accountFrom.privateKey
);
// 8. Send tx and wait for receipt
const createReceipt = await web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(
createTransaction.rawTransaction
);
console.log(`Tx successful with hash: ${createReceipt.transactionHash}`);
};
// 9. Call reset function
reset();
View the complete script
// Import Web3 and the contract abi
const Web3 = require('web3');
const { abi } = require('./compile');
// Add the Web3 provider logic here:
const providerRPC = {
evmNetwork: 'https://services.tanssi-testnet.network/dancelight-2001', // Insert your RPC URL here
};
const web3 = new Web3(providerRPC.evmNetwork);
// Create variables
const accountFrom = {
privateKey: 'INSERT_YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY',
};
const contractAddress = 'INSERT_CONTRACT_ADDRESS';
// Create Contract Instance
const incrementer = new web3.eth.Contract(abi, contractAddress);
// Build reset tx
const resetTx = incrementer.methods.reset();
// Create reset function
const reset = async () => {
console.log(
`Calling the reset function in contract at address: ${contractAddress}`
);
// Sign tx with PK
const createTransaction = await web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction(
{
to: contractAddress,
data: resetTx.encodeABI(),
gas: await resetTx.estimateGas(),
},
accountFrom.privateKey
);
// Send tx and wait for receipt
const createReceipt = await web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(
createTransaction.rawTransaction
);
console.log(`Tx successful with hash: ${createReceipt.transactionHash}`);
};
// Call reset function
reset();
To run the script, you can enter the following command in your terminal:
node reset.js
If successful, the transaction hash will be displayed in the terminal. You can use the get.js script alongside the reset.js script to make sure that the value is changing as expected.
| Created: September 1, 2023