Tanssi Staking for Block Production¶
Introduction¶
One of Tanssi's core propositions is to simplify the infrastructure complexity for networks. A significant component is bootstrapping a decentralized set of sequencers, which Tanssi offers through its unique architecture and staking mechanics.
Tanssi staking mechanics guarantee that the sequencers for Tanssi-powered networks are selected through a trustless and decentralized mechanism. They also incentivize the community to delegate to top-performing or engaged sequencers.
This page covers the fundamental concepts of Tanssi's staking mechanics and how it secures a decentralized block production set that drives network liveness for Tanssi networks.
Core Concepts¶
Tanssi's staking module mechanics were inspired by the concept of liquidity pool tokens (LP tokens) in traditional Automated-Market-Makers (AMMs) like Uniswap V2.
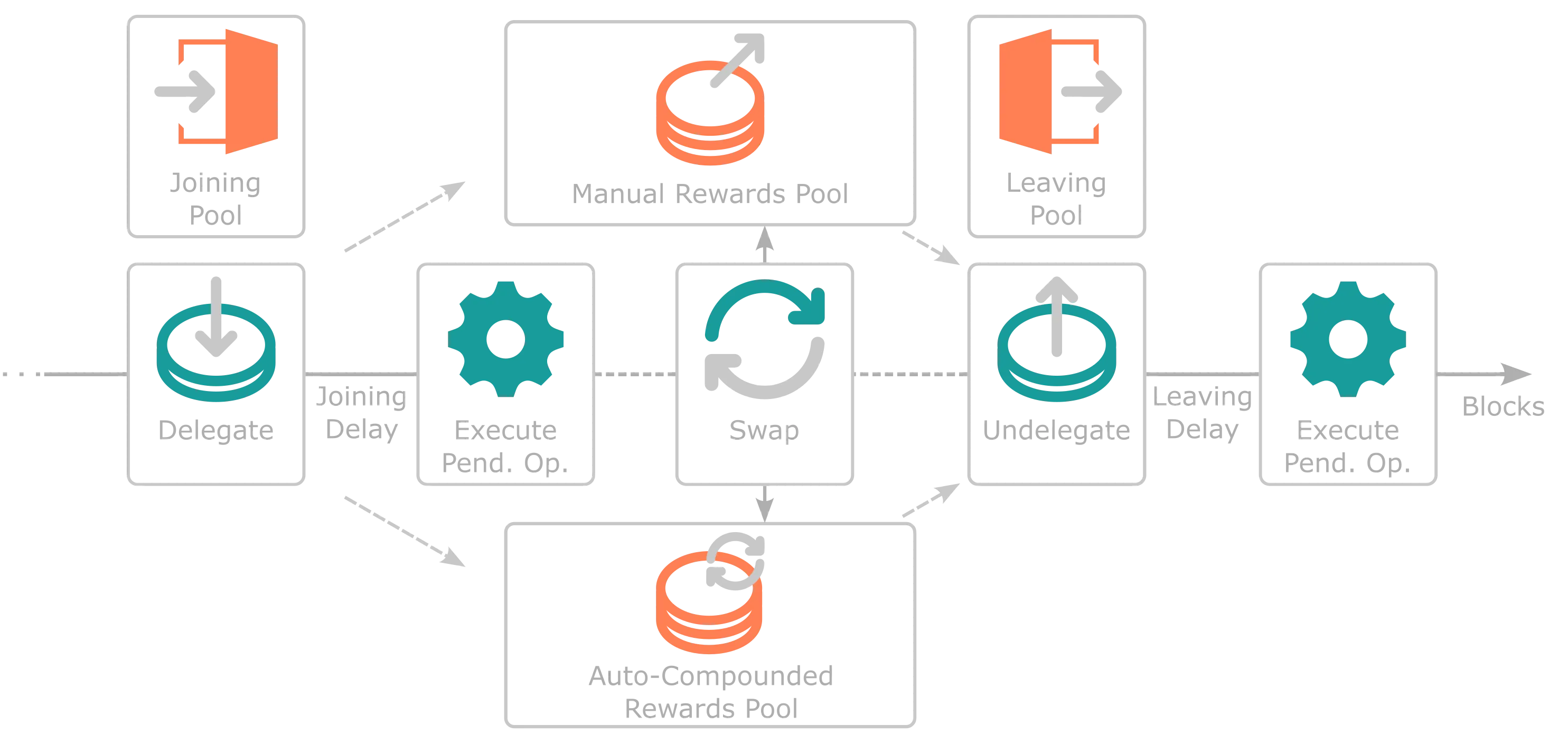
Each sequencer has four liquidity pools through which delegators move as they perform different staking operations. In short, each liquidity pool represents a different state throughout the staking process: joining, staking through manual rewards, staking through auto-compound rewards, and leaving. Nevertheless, one core difference is that LP tokens in common AMMs are transferable while staking shares tokens are not.
A delegator has four simple transactions to go through the different states (liquidity pools): delegate (for manual or auto-compound rewards), undelegate, swap, and execute pending operations. For example, users who want to stake through either rewards pool can use the delegate call and join the Joining Pool immediately. After a delay, users (or anyone else) can execute the pending operation and enter the initially set rewards pool. Once there, users can swap between reward pools as often as they like. Lastly, users in a rewards pool can use the undelegate call to go into the Leaving Pool and unstake their tokens (or anyone else's) executing the pending operation after a given delay.
Liquidity pools have a set of shares that can be considered LP tokens in traditional AMMs. When users join a new liquidity pool, they are given several shares (LP tokens) that depend on the pool type, the number of tokens they staked, the total number of shares, and the total number of tokens staked in that pool.
Rewards are assigned to a sequencer's Manual or Auto-Compound Reward Pools when Tanssi attests that the specific block production slot that sequencer was assigned to has been fulfilled, and the block was produced successfully.
All rewards (for all pools) are stored in a protocol-owned account. Nevertheless, the protocol internally keeps track of the actual native tokens held by each pool. The core difference between staking through the Manual or Auto-Compound Rewards Pools is how rewards are distributed. In the Manual Rewards Pool, users have to claim any staking rewards they've accumulated manually. In contrast, in the Auto-Compound Rewards Pool, the rewards are automatically re-staked at each Tanssi block, where the protocol announces the sequencer for each block production assignment.
The delegate and undelegate operations need to be sent by the delegator itself. They signal the intent of the action to be taken and ask the protocol to perform the necessary checks to allow the delegator to delegate or undelegate. Consequently, these actions can be executed only after a certain number of sessions, but anyone in the network can perform this second operation through the execute pending operation transaction.
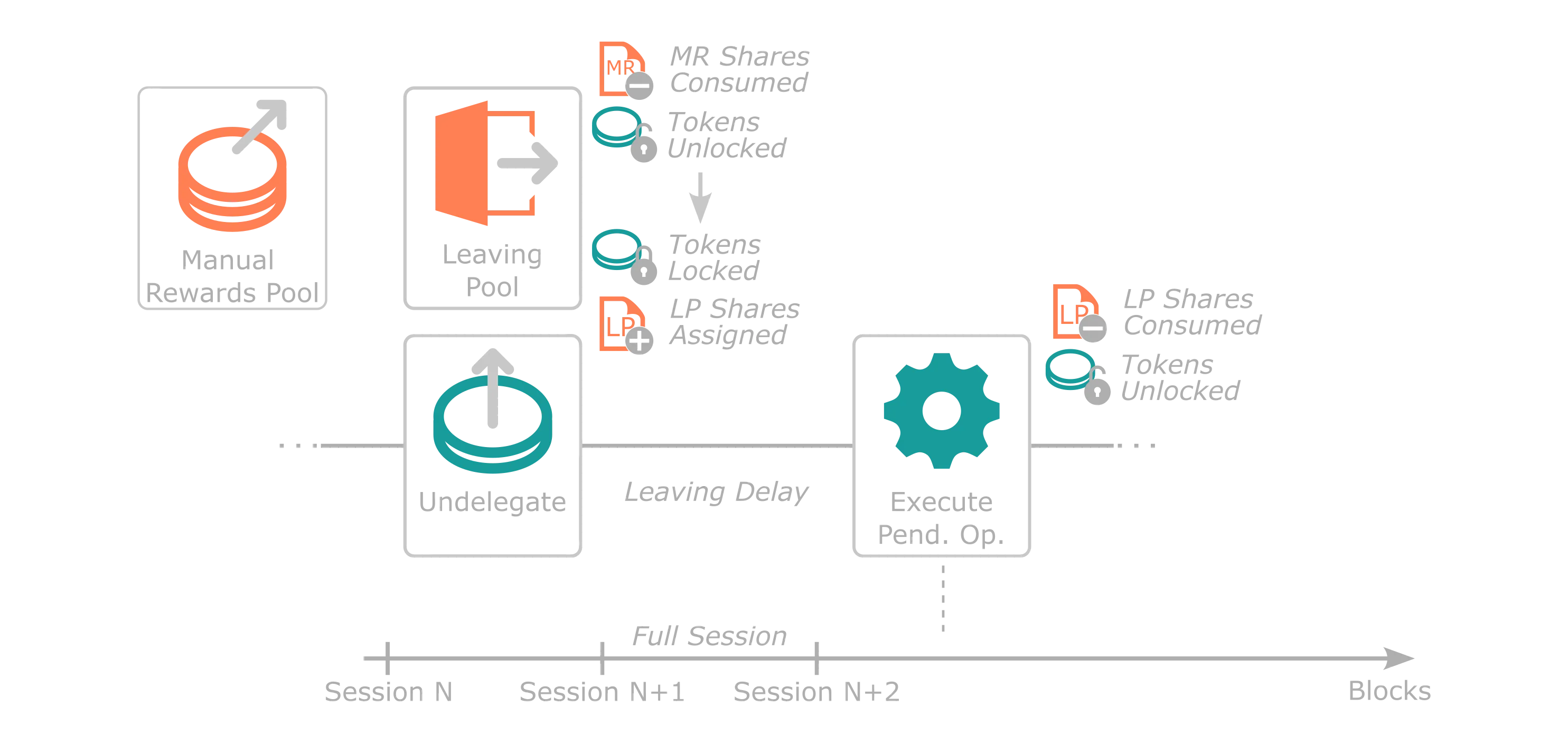
The following diagram summarizes the high-level flow of a delegator delegating and undelegating tokens to a sequencer. User actions are highlighted in cyan, while different pools are highlighted in coral.
Staking Parameters¶
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Joining Delay | 7200 blocks (12 hours) |
| Leaving Delay | 7200 blocks (12 hours) |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Joining Delay | 7200 blocks (12 hours) |
| Leaving Delay | 7200 blocks (12 hours) |
Staking Pools¶
The following section goes through each of the liquidity pools that represent a step throughout the staking process.
Joining Pool¶
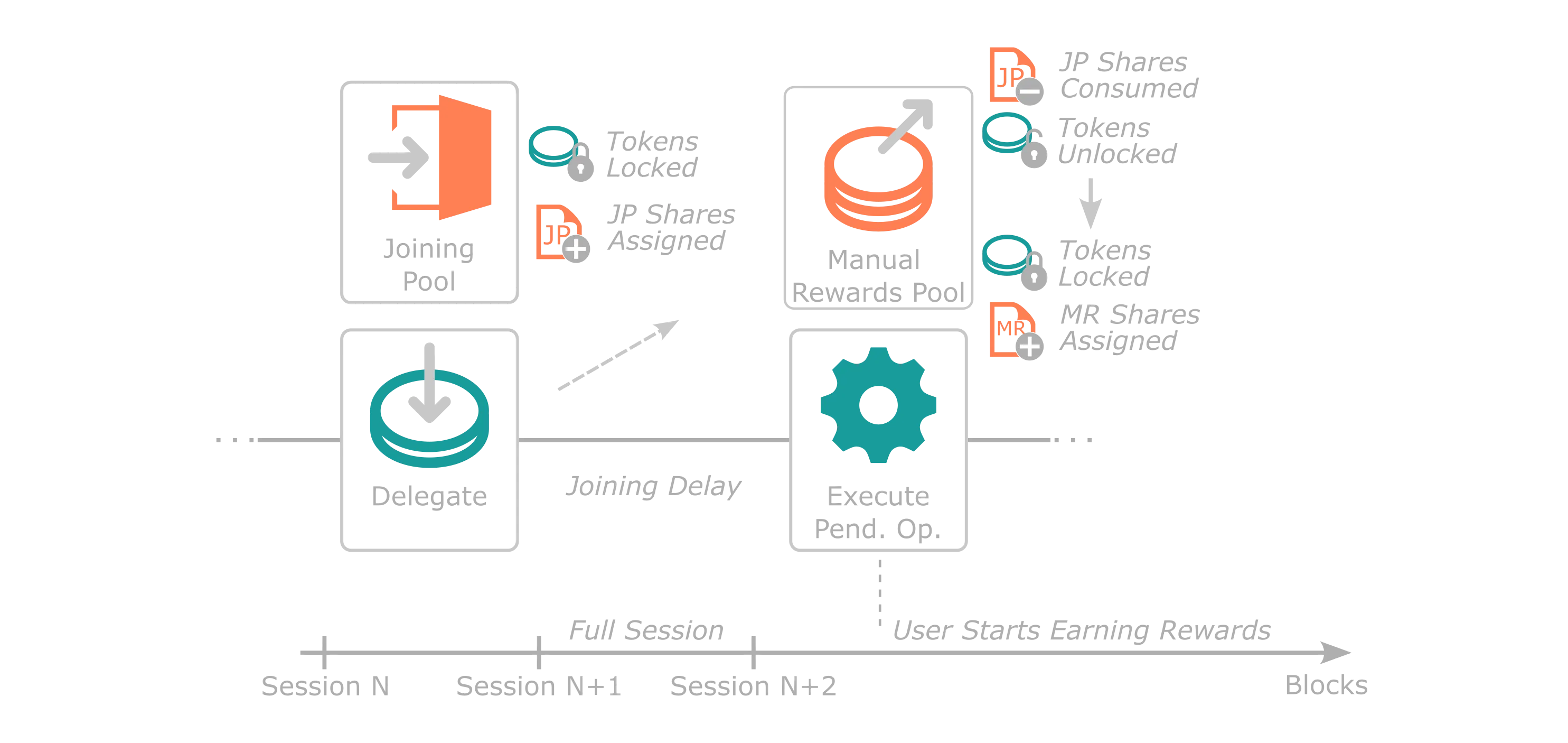
When a user first delegates to start the staking process, it must state what staking rewards mechanism it wants: manual or auto-compound rewards (each being a separate pool). Once the joining transaction is executed, the user automatically enters the Joining Pool and is given shares of that pool directly correlated to the number of tokens being staked. This pool offers stability to the current set of sequencers by providing a delay between a delegator staking and receiving rewards. The delay is set to at least one entire session.
As a practical example, Alice starts the staking process targeting the Manual Rewards Pool and enters the Joining Pool halfway through a session; she must wait until the end of the next session to execute her pending operation to start receiving staking rewards.
Joining Pools for each sequencer have a one-to-one ratio of shares per token staked. Therefore, if Alice is staking 100 tokens, she will receive 100 shares (LP tokens) of the Joining Pool she entered. When her delegate pending operation is executed, the protocol consumes her shares of the Joining Pool in favor of native protocol tokens, which are immediately swapped to shares in either the Manual Rewards or Auto-Compound Rewards Pools.
The following diagrams assumes a user is staking into the Manual Rewards Pool.
Manual Rewards Pool¶
When a user joins the Manual Rewards Pool, the protocol destroys all Joining Pool shares they own in favor of the native protocol token. Next, in the same block, the protocol computes the amount of Manual Pool shares that can be minted with this amount based on the share's price. The price is calculated based on current pool conditions, that is, the number of native tokens and shares that exist:
SharePrice [Tokens/Shares] = NumberOfTokensInPool / NumberOfSharesInPool
Shares don't have decimals. Consequently, any remaining native tokens when acquiring the pool's shares are refunded to the user. The share price is not impacted by users joining the pool, as the ratio is maintained. Once the user has Manual Rewards Pool shares, they earn staking rewards (that is, in the same session) that need to be claimed manually by the user delegating.
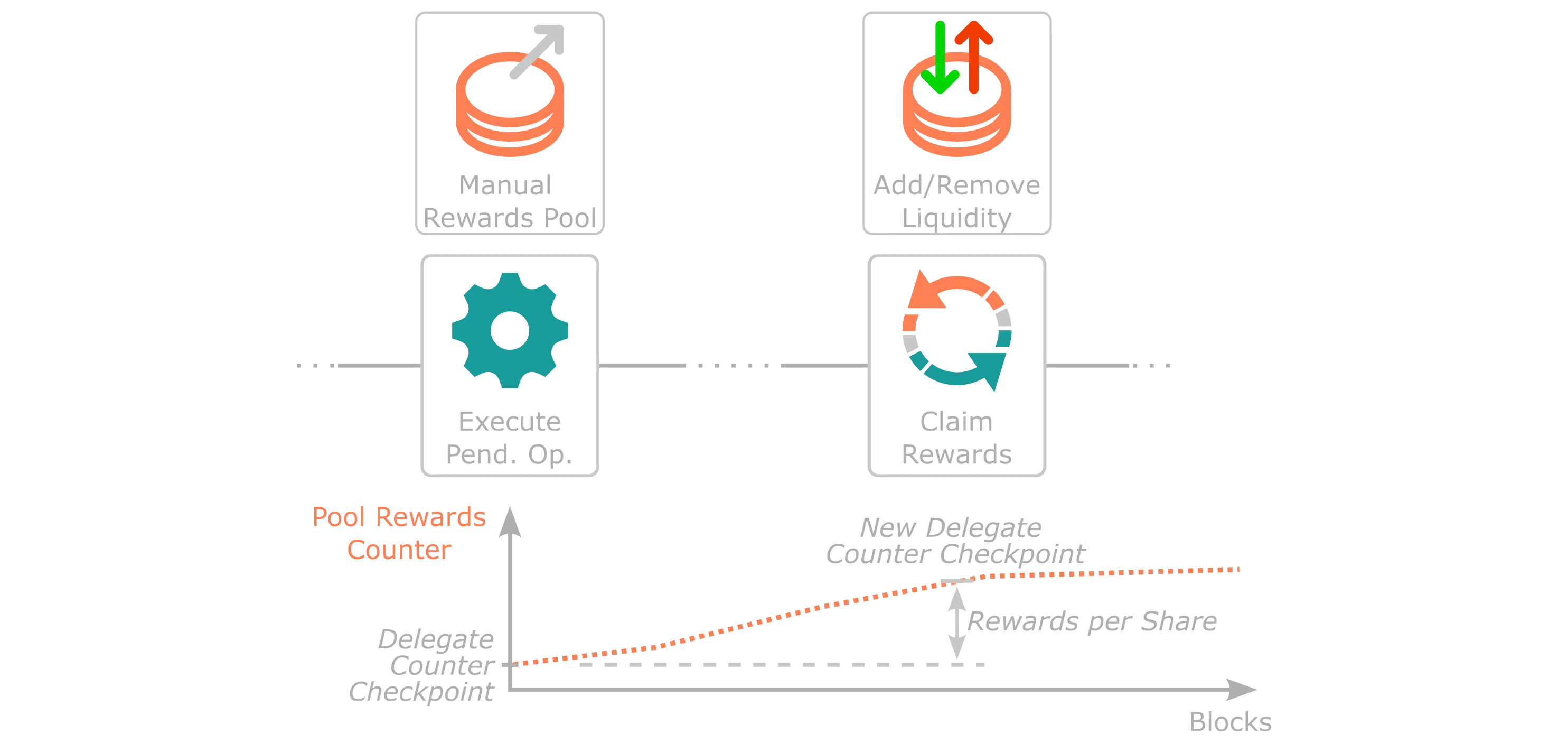
In contrast to the Auto-Compound Rewards Pool, where reward distribution is done automatically to the specific pool, the distribution for the Manual Rewards Pools operates through a counter checkpoint rewards mechanism. This mechanism tracks the historical native token per share distribution rate assigned to you by the protocol for that particular Manual Reward Pool at a specific point in time. When Tanssi attests that a block was produced by a given sequencer, new rewards are assigned to that Manual Rewards Pool for users to claim, and the rewards counter increases. Therefore, rewards are reflected as the ratio of native tokens per share you receive as staking rewards, which is the difference between the current pool's rewards counter and your original rewards counter checkpoint.
Consequently, the native tokens per share rewards counter plays a vital role in the protocol's calculation of the tokens the user is due when they claim their rewards. Once the rewards are calculated, the protocol sends them from the protocol-owned account to the user. Simultaneously, the user's rewards counter checkpoint is reset to the current one set by the pool current counter value. This reset is necessary to ensure the user's new rewards counter aligns and that the due rewards are zero.
Similarly, when a user stakes or unstakes tokens, rewards are automatically claimed, and the user's checkpoint rewards counter is reset. Adding or removing a stake means that reward conditions for that specific amount differ from what the protocol has in storage. Consequently, the rewards counter checkpoint must be synced with the pool's rewards counter to ensure no imbalances.
Auto-Compound Rewards Pool¶
When a user joins the Auto-Compound Rewards Pool, the protocol destroys all Joining Pool shares they own in favor of the native protocol token. Next, in the same block, the protocol computes the amount of Auto-Compound shares that can be minted with this amount based on the share's price. The price is calculated based on current pool conditions, that is, the amount of native tokens and shares that exist:
SharePrice [Tokens/Shares] = NumberOfTokensInPool / NumberOfSharesInPool
Shares don't have decimals. Consequently, any remaining native tokens when acquiring the pool's shares are refunded to the user. The share price is not impacted by users joining the pool, as the ratio is maintained. Once the user has Auto-Compound Rewards Pool shares, they earn staking rewards (that is, in the same session).
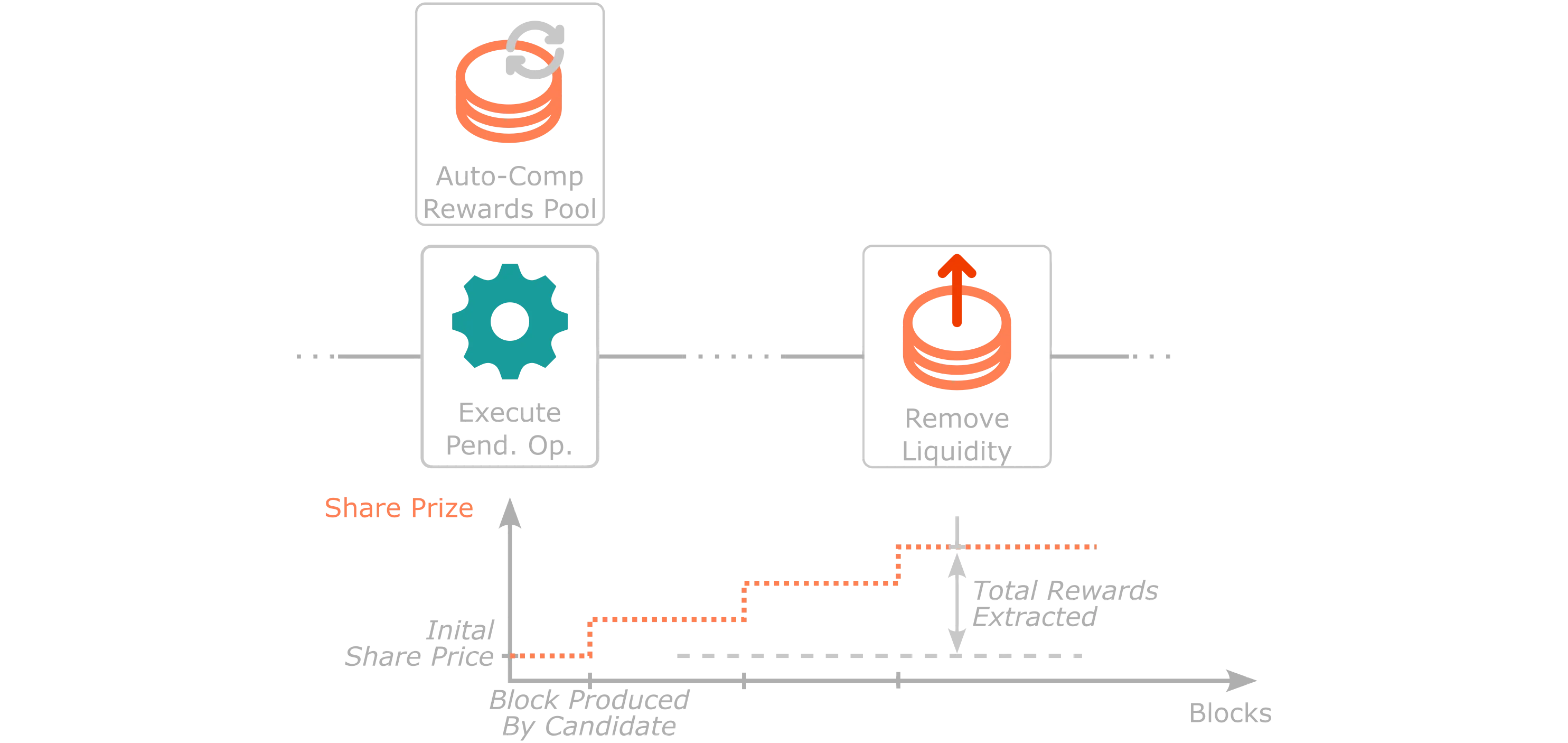
In contrast to the Manual Rewards Pool, native token rewards in the Auto-Compound Rewards Pool are automatically assigned to the pool at each Tanssi block where the protocol attests the sequencer for each block production assignment in any Tanssi-powered network. Consequently, as the number of native tokens held in the pool increases but the number of shares stays constant, the share price increases (according to the formula). Therefore, if the users redeem their shares for native tokens, they will receive more native tokens per share than when they joined the pool.
Native token rewards are automatically assigned as new stake into the Auto-Compound Rewards Pool, hence the auto-compounding nature of this specific staking pool mechanism.
Nevertheless, when auto-compound staking rewards are assigned, they are not held in the user's reserved balance, as the protocol-owned account still has them. The increase in the delegator's stake is indirectly represented by the share price increase. However, in specific scenarios, a user might want to let the protocol know that they want that balance to be represented in their state as reserved balance, for example, for governance purposes.
Consequently, the protocol offers a specific transaction any user can submit to update the reserve balance of any delegate. This call moves the auto-compound rewards for the specified user from the protocol-owned account to their reserve balance. This is also automatically executed by the protocol when a user removes liquidity from a Auto-Compound Rewards Pool.
Leaving Pool¶
When a user decides to exit their staking positions from a Manual or Auto-Compound Reward Pool, they have the power to initiate an undelegation. This process, similar to when they initially entered the Joining Pool, is a two-step journey. The user signs an intent to remove a specific delegation and patiently waits for at least one entire session before the operation can be executed by anyone.
Upon executing the leaving transaction intent, the protocol exchanges shares of the specified pool for native tokens at the current pool price. For the Manual Rewards Pool, any unclaimed rewards are assigned to the user. Simultaneously, the protocol purchases Leaving Pool shares in a one-to-one ratio for the native tokens the user just received. This ensures that the user joins the Leaving Pool, acquiring shares that correspond to the number of native tokens they desire to unstake.
After an entire session passes, any user can execute the pending operation. Then, the protocol swaps Leaving Pool shares for native protocol tokens at a one-to-one ratio.
The primary purpose of the Leaving Pool is to provide a buffer for users leaving the staking mechanics. This buffer allows the implementation of slashing mechanisms to deter bad behavior. Slashing has not been implemented in Tanssi but could be implemented in the future.
The following diagrams assumes a user is unstaking from the Manual Rewards Pool.
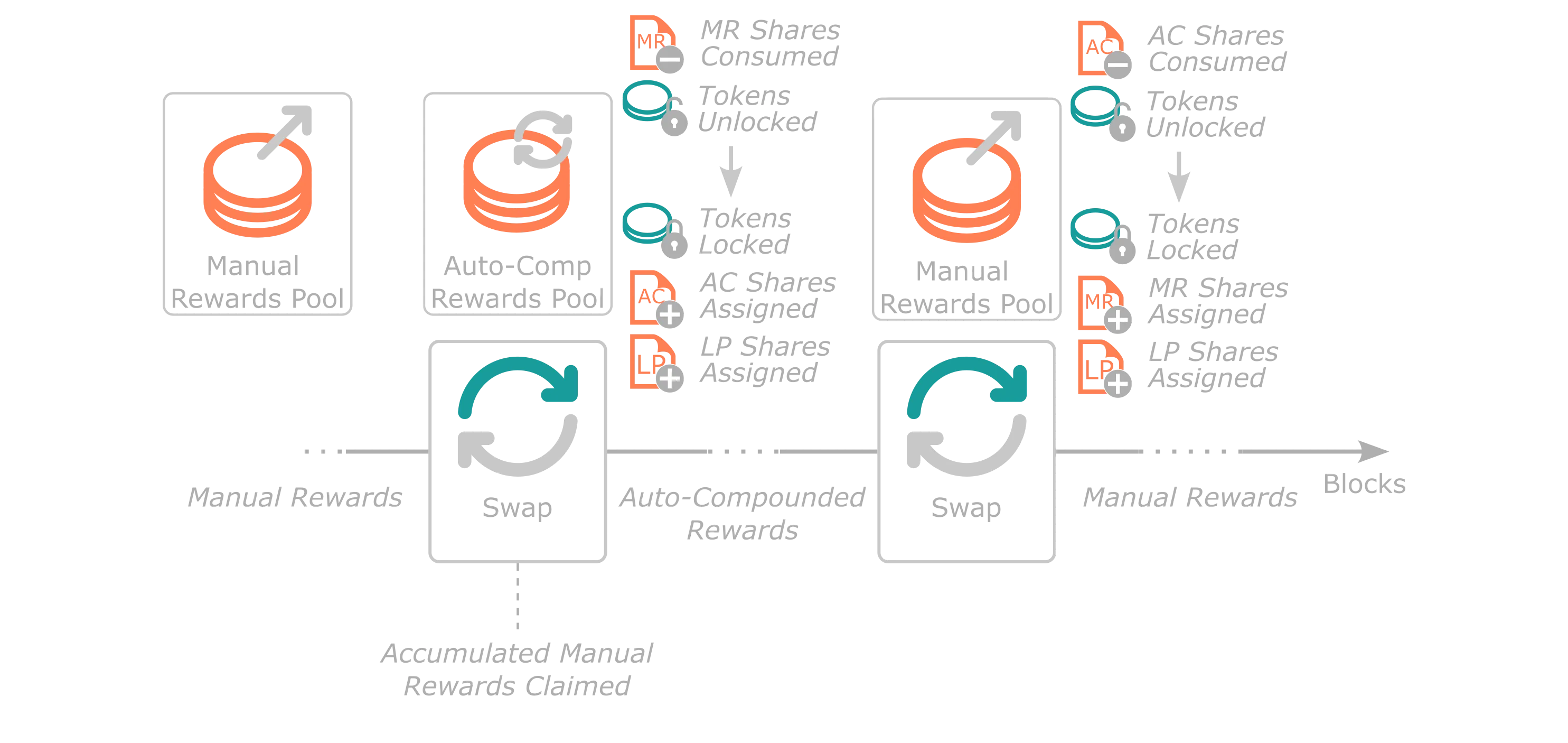
Swapping Between Rewards Pools¶
Tanssi's staking module allows users to swap their stake from one type of reward pool to another. Users can use this functionality to move partial or full amounts of the staked tokens in a specific pool. The main benefit is that users don't have to go through the Leaving Pool and the Joining Pool again to move their stake.
First, all pending Manual Rewards Pool rewards are claimed at a protocol level, as liquidity is either added or removed. Therefore, the checkpoint rewards counter needs to be synced with the pool. Next, shares from the original pool are consumed and exchanged in favor of native protocol tokens at the current pool price. Then, shares of the new pool are attained at that pool's price. Lastly, any dust tokens remaining are automatically exchanged in favor of Leaving Pool shares. Note that all of the above is executed in the same block, and users don't have to wait for delays to earn rewards in the new pool. The dust in the Leaving Pool can be claimed after the required delays have passed.
| Created: February 22, 2024